Overview
MTSN is a multi-port, multi-rate managed Ethernet switch with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) capabilities to achieve deterministic Ethernet solutions in which streams are delivered with guaranteed bandwidth and deterministic latency.
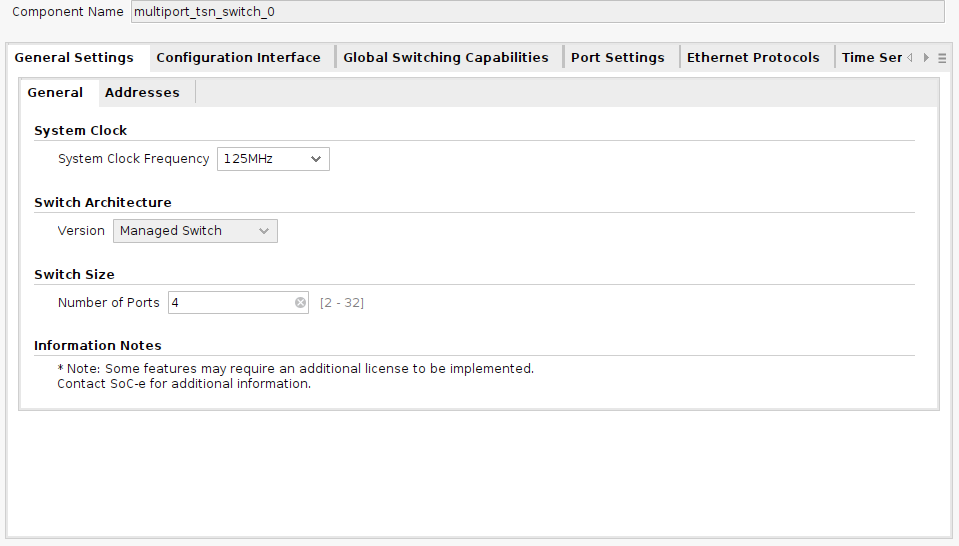
With a rich set of layer-2 configurable features, both at synthesis time & during runtime, MTSN allows building advanced Ethernet switch systems with TSN capabilities. MTSN switch has been designed to address the maximum throughput using optimized resources.
All these characteristics enable a wide number of applications/sectors where the use of MTSN IP Core is key. Automotive, Marine, Aerospace, Defence or Electric are examples of markets where our customers are already applying this technology.
Key Features
- Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) Support
Aligned with the different TSN profiles, such as Aerospace (P802.1DP), Automotive (P802.1DG) or Industrial Automation (IEC/IEEE 60802).
- Ethernet Switch IP “builder”
Hundreds of user-configurable parameters allow obtaining the exact switch configuration required by the customer, ensuring efficient use of the available programmable logic resources.
- Different Data-rate Per Port
Each port speed and interface can be assigned independently.
- High-performance
Up-to 1G interfaces without HOL (Head-of-line) blocking effect.
- Fast & Smooth Integration
GUI available for some FPGA vendor tools (i.e., AMD Vivado™ Design Suite). Drivers & software components included as part of the product deliverable.
- Evaluation Version Available
Encrypted, time-limited version available.
Technical Specifications
Communication Interfaces
- Integrated 10M/100M/1000M MACs for 10/100 Mbps and 1 Gbps PHY interface rates to use with any PHY interface type (e.g. MII, RMII, GMII, RGMII) depending on application
- Compatible with SGMII (Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface) or QSGMII (Quad Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface) PHY interfaces throughout an internal GMII based connection to AMD LogiCORE™ SGMII IP core and LogiCORE™ QSGMII IP core respectively
- 10/100/1000 Mbps AXI-Stream interface with a data width of 8 bits @ 125 MHz
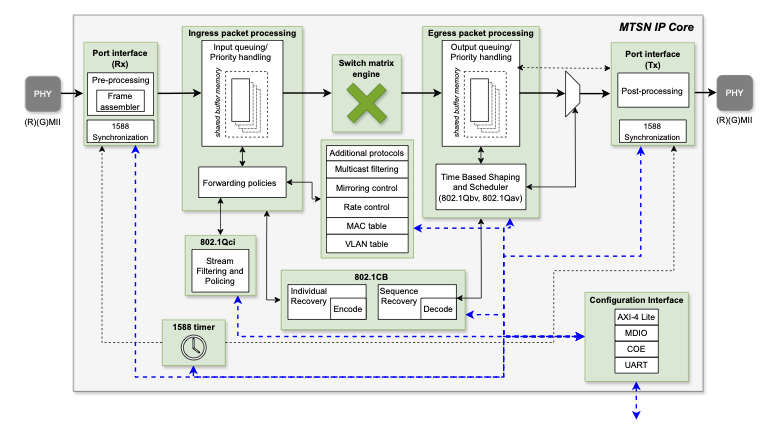
Time Sensitive Networking (TSN)
- TSN features can be enabled/disabled independently
- IEEE 802.1AS – Timing and Synchronization
- IEEE 802.1Qav – Credit Based Shaper (CBS)
- IEEE 802.1Qbv – Time Aware Shaper (TAS)
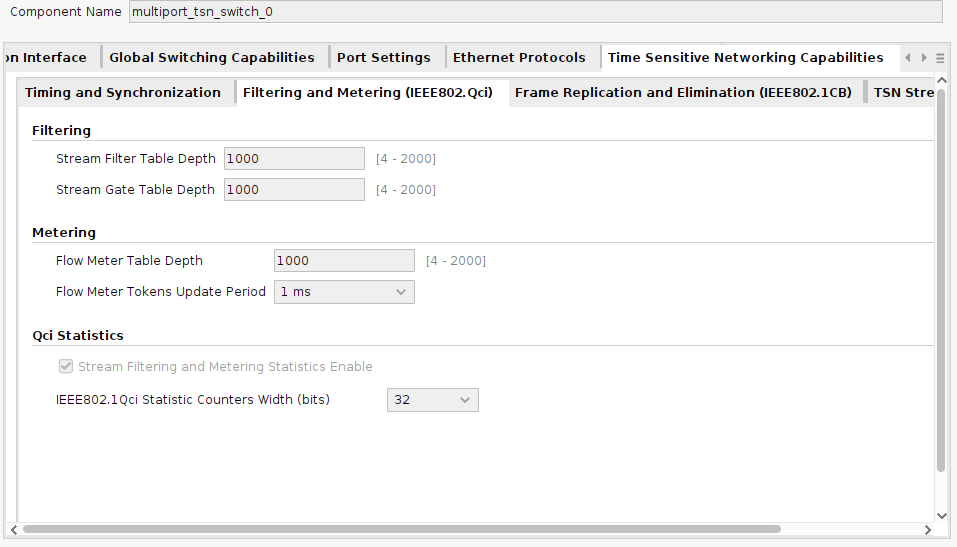
- IEEE 802.1Qci – Per-Stream Filtering and Policing
- IEEE 802.1CB – Frame Replication and Elimination for Reliability (FRER)
- IEEE 802.1Qbu / IEEE 802.3br – Frame Preemption
- IEEE 802.1Qcc – Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP) Enhancements and Performance Improvements
Time Synchronization
- Time Synchronization according to IEEE 802.1AS-2020 and IEEE1588 (PTP)
- Up to four IEEE 802.1AS time domains
- Legacy PTP: IEEE 1588 Boundary Clock (BC) at layer-2 and layer-3 (IPv4)
Traffic Management
- Integrated Ethernet switch fabric supporting up to 32 ports (number limited by the available resources on the device)
- HoL (Head-of-Line) blocking free switch fabric
- Shared Dynamic and Static Filtering Database. Implements hardware MAC address learning/ageing and look-up for up-to 9K absolute MAC addresses (synthesis scalable) at wire speed
- Independent VLAN Learning support for MAC address learning
- Searchable MAC addresses (and associated information) contained in the Filtering Database
- Programmable Frame Forwarding port mask to restrict frame forwarding towards port(s)
- Programmable Ethertype based Frame Forwarding to restrict frame forwarding towards port(s)
- Static Multicast frame filtering
- IGMP v1/v2 Snooping1 (IPv4) support for multicast frame filtering
- Standard frame size support (1518 bytes) or Jumbo frames up to 9 kByte (depends on memory availability)
Quality of Service
- Up to 8 priority queues per port (synthesis option)
- Priority classification based on ingress port, PCP bits (802.1p), DSCP TOS bits of the IP packets (IPv4 TOS / IPv6 COS) and EtherType
- Programmable remapping from PCP or DSCP fields to internal priority queues on a per-port basis
- Programmable Priority Regeneration on a per-port basis
- Egress traffic prioritization based on Strict priority or Weighted Round Robin (WRR) scheduling algorithm
- IEEE 802.1Q tag-based and Port-based VLANs. VLAN manipulation functions on reception (VLAN insertion) and transmission (VLAN removal/overwrite)
- MAC Level Ingress Frame Filtering based of Destination MAC address and/or Ethertype on per port basis
- Token Bucket based Ingress Throughput Rate Limiting on per port basis
- MAC Level Ingress Frame Rate Limiting on per port basis
- Credit Based Shaper (CBS) egress throughput rate Limiting on per port basis
- Egress Frame Rate Limiting on per port basis
- Broadcast/Multicast storm protection
Network Management & Monitoring
- IEEE 802.1D Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent loops from being formed when switches or bridges are interconnected via multiple paths
- IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) provides rapid convergence of spanning tree
- IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) provides link availability in multiple VLAN environments by allowing multiple spanning trees
- Multisession port mirroring capabilities. Ingress and Egress mirroring functions to allow copying of frames to a mirror port. Option for mirroring only filtered frames that match a specific data pattern
- User/network port-level security via IEEE 802.1X authentication and MAC-based filtering
- Host access control for only frames specified by the user (destination MAC and/or Ethertype based).
- Per port MAC and switch statistics for managing and debugging purposes
- Wide range of management interfaces to access control and statistics registers (selectable at synthesis time)
- I2C master interface for external device configuration (i.e. an EEPROM memory with non-volatile configuration)
Others
- Distributed Switch Architecture (DSA) frame tagging to merge application specific messages to management port and to distribute application specific messages to a specific port
- Exclusive forwarding of known protocol specific frames or custom frames to/from management port
Technical Support, Verification & Deliverables
Technical Support
IP Licenses are provided along with a Technical Support package that ensures a direct communication channel with our highly experienced support engineers. This is vastly valued during customer product development & integration phases.
Verification
All our IP Cores are rigorously tested, hardware-validated and verified in real-life environments. A 3-phase based IP product verification is applied:
- Entity/Block-oriented simulation
- Global-oriented simulation
- In-hardware validation
Deliverables
- Encrypted/Source RTL code
- Software components: Drivers, configuration API & SW stacks
- Documentation (IP Core and Software components)
- (Optional) Networking Testbench Suite (NTS)
- (Optional) AMD Vivado™ design suite example design
Evaluation & Design-in Kit
In order to evaluate MTSN in a plug&play platform please refer to our RelyUm Industrial TSN Switches and Endpoints product family. You can check out all the details through the following page:
https://soc-e.com/relyum-industrial/tsn-switches-and-endpoint-switches/